Returning to his home state of Utah, where more babies are born with cleft lip and palate than is typical, Dr. Devan Griner made plans to open his own practice, joining the small cohort of plastic surgeons nationwide who treat the condition.
As he recruited doctors to fill out a team in 2017, Griner had lunch with an orthodontist who’d long worked in the state. He quizzed Griner on his credentials and then turned to bone grafting, a common procedure for cleft patients, who are often missing a piece of their upper jaw. Sitting back, the doctor looked hard at Griner and lobbed a test question: At what age would Griner do bone grafts on patients?
It was a surprising question. There is broad consensus nationwide to time bone grafts to when a patient is getting certain adult teeth, and so Griner, a bit taken aback, replied that of course he does it then. That’s when Griner said the orthodontist relaxed, leaned in over their Neapolitan pizza and declared, “We have a bone grafting problem here in Utah.”
Almost immediately Griner encountered it for himself. Patients began turning up who’d had treatment that departed from the standard of care in ways Griner found alarming. In many cases, he felt they’d had, or been advised to undergo, grueling, and possibly unnecessary, facial surgeries earlier than his profession advised. And they were all treated at Primary Children’s Hospital in Salt Lake City.
As more former Primary Children’s patients sought out Griner’s team, the doctors started to question among themselves, and then with other cleft doctors in the state, whether they needed to do something. It’s a rare and risky move to call out a fellow doctor’s work, much less a team at a well-known hospital. Most children born with a cleft in the five-state region around Utah are treated at Primary Children’s, some traveling the farthest distance for care in the nation. It’s the largest pediatric hospital in the area, and for many, it had been the only choice.
A crucial question emerged: Did the hospital’s patients, and their anxious parents, know that the care they were getting at Primary Children’s was different from what cleft surgeons at top hospitals around the country provided?
The question hit at the heart of a common tension in medicine between the sort of innovation that drives life-enhancing advances and the accepted standard of care, which is informed by peer-reviewed medical studies, broad agreement among specialists and insurance company policies. What information are patients, especially children, owed? And how should regulators respond when doctors want to try something new — especially when doctors, and their choices, may be geographically or otherwise isolated from their peers?

Credit:
Hannah Yoon, special to ProPublica
In the case of cleft lip and palate, the future of children’s faces are on the line. The success of some cleft procedures isn’t fully known until a child has finished growing. Although there can be signs along the way, not until cleft patients are almost adults will doctors be able to fully assess if a certain treatment done at 2 years old was ultimately beneficial or harmful.
Griner’s team and other doctors who’d worked in Utah eventually felt they had to take collective action. A group of nine doctors decided to file a formal complaint with the state, saying “this is about protecting children.” Among their allegations: Some doctors on the hospital’s cleft team were performing bone grafts on patients who were too young — around age 2 — and using an off-label, controversial bone growth product that many doctors shun. They were performing intensive jaw surgeries — which require children to wear a large metal device screwed into their heads for months — so early that they risked some children needing to repeat the operation. And the team was performing surgeries some patients didn’t need.
“They just over, overoperate,” said Lisa Morris, one of the cleft doctors on the state complaint.
Cleft specialists at seven large pediatric institutions around the country, including Seattle Children’s Hospital and Nationwide Children’s Hospital, told ProPublica that the way doctors performed several procedures sharply departed from their speciality’s most common practices.
Utah’s Division of Professional Licensing is investigating the practices of several doctors on Primary’s cleft team, which is staffed by University of Utah doctors. The state agency originally closed the complaint with little investigation, but after an appeal to the head of Utah’s commerce department, which oversees licensing, the division reopened it in April.
Dr. Dana Johns, director of Primary Children’s cleft team, said the fact that her team’s practices don’t align with those of her colleagues in the field “doesn’t mean that different is wrong.” She said that intervening earlier helps protect children with visible facial differences from a gamut of bullying in their formative teen years.
In interviews, both Primary Children’s and the University of Utah told ProPublica they stand by their protocol and fully inform their patients during appointments about how and why their care differs. What the team does is “clinically defensible and potentially advantageous,” Kathy Wilets, a University of Utah Health spokesperson, wrote in a statement.
But ProPublica’s questions, the hospital said, prompted the hiring of two independent cleft surgeons to formally review the protocol. Bioethicists have also reviewed the hospital’s informed consent procedures, leading administrators to make changes to its cleft consent policies and consider hospitalwide changes.
Dr. Jay Agarwal, the hospital’s chief of plastic surgery, said the cleft team believes the standard methods of treating cleft lip and palate aren’t good enough and is trying to advance care by fixing children’s mouths at younger ages and in ways that could eliminate the need for surgery when they’re older.
“We always have to try to do better,” he said.
But parents of some of Primary Children’s patients say their children were unwitting participants in what the hospital calls innovation and what some other cleft experts deemed a potentially risky deviation from evidence-based treatment. Experts said bone grafts done at such an early age could stunt facial growth, resulting in the upper lip looking pushed back and impairing basic tasks such as talking and chewing.
The final results of the early bone grafting won’t be known for years. Patients treated under the new bone-grafting protocol Primary Children’s started around 2017 won’t start seeing full outcomes until around 2029.
Emily Rogers still feels the burden of remorse six years after her son’s bone graft when he was 21 months old. She, like members of several families ProPublica spoke with, said the former head of the program didn’t tell her that bone grafting at that age was unusual, that the hospital was just starting to try it or that doctors weren’t sure how her son’s face would grow after the procedure.
“It’s sickening to find out later you put your kids in their hands and they lied to you, basically,” she said. “That’s what it feels like: It was a lie.”

Credit:
Hannah Yoon, special to ProPublica
The Standard of Care
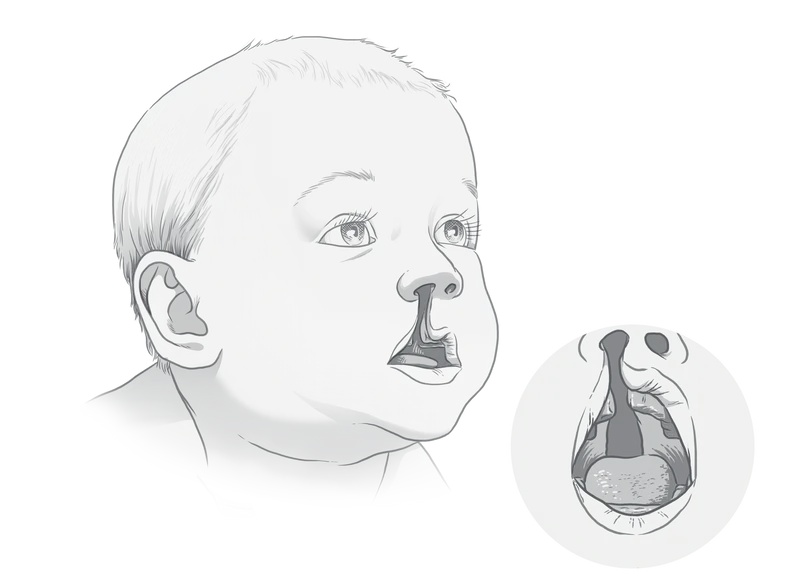
From the time a cleft is spotted on a sonogram during pregnancy, parents begin prepping for a series of surgeries to help their child with a noticeable facial difference. Each step of care throughout childhood builds upon the last, slowly marching the face toward the form it failed to take in the womb. A doctor’s misstep can veer the mouth off course or mean more surgery.
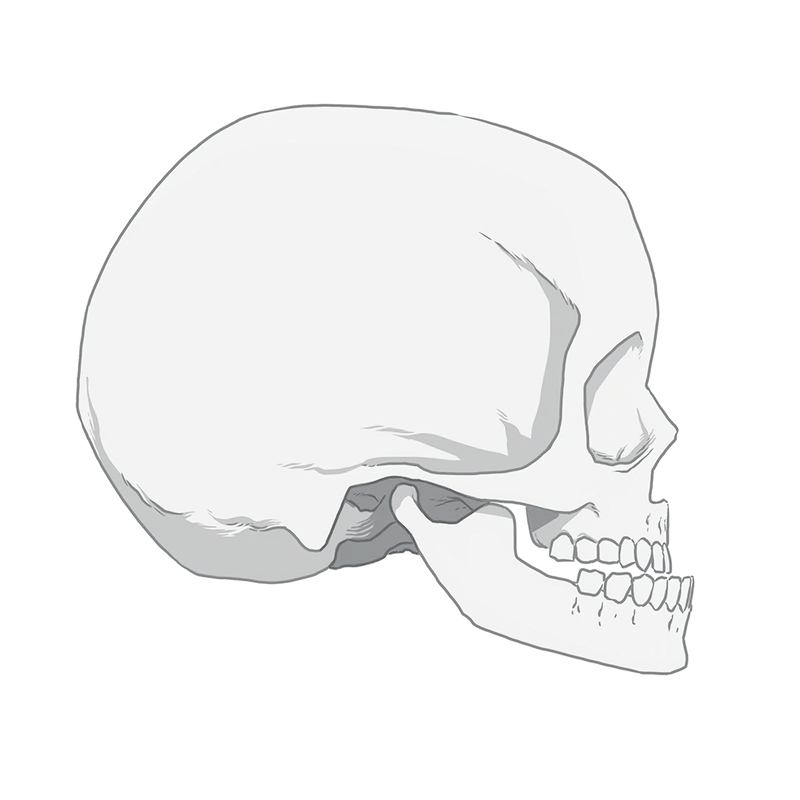
People unfamiliar with clefts, besides perhaps what they’ve seen on Operation Smile fundraising commercials, tend to think of the treatment as a one-and-done surgery to repair a small slit in the lip. And while that can be the case, for a lot of babies born with the condition, it’s much more involved. Often, a wide split starts at the nostril, goes down the lip, runs through the upper jaw and continues back through the roof of the mouth toward the throat. Sometimes there are splits on both sides of the mouth.
Cleft lip and palate together affect about 1 in 1,600 babies in the U.S.; around 2,500 are born with both each year. It is unclear why Utah has a higher rate. In general, the cause of a cleft is not well understood. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, there is some evidence that genetics can play a role, and some environmental factors, such as smoking during pregnancy or taking certain medications, can increase the chances of a cleft forming, which happens in the first trimester.

Credit:
Illustration by Matt Twombly for ProPublica
A cleft can affect a child’s teeth, position of the midface and nose, and ability to hear, breathe, swallow and speak. Many cleft patients need care from a range of specialists from their earliest days until adulthood. Successful cleft treatment repairs those issues, leaving patients’ faces with little evidence of their cleft issues by the time they are grown.
Like most well-known conditions, there is a treatment plan for cleft lip and palate that a majority of doctors follow, known generally as the standard of care. ProPublica spoke with more than a dozen cleft specialists nationwide, and all acknowledged the variability, subjectivity and debate in cleft care. Several pointed out there aren’t large randomized trials that have definitively provided answers, and care continues to evolve. Still, they all laid out the same general timeline of cleft treatment and the reasons for it.
Doctors usually repair the lip and nose around 3 to 6 months, close the palate around 9 to 18 months and then wait to do a bone graft until children are about 5 to 11 years old, though there is debate about when in that age range is best. Jaw surgery, if needed, typically waits until the child is done growing. Most patients will need rhinoplasty and years of orthodontia as well and, in some cases, additional surgeries to help with things like speech.
Richard Kirschner, chief of plastic and reconstructive surgery at Nationwide Children’s in Ohio and the editor of a widely used cleft textbook, said this timeline is based on evidence collected over decades in the care of thousands of patients.
To the doctors at Primary Children’s, the skepticism they’re facing is the plight of pioneers.
“I think it’s easy to keep doing things the same way in the way they’ve always been done,” said Agarwal, who noted that he doesn’t think there is a standard of care in cleft. “And, you know, that’s the answer for a lot of groups that they feel like they don’t want to try new things. And that’s OK. I mean, nothing’s wrong with that.”
Credit:
Kim Raff, special to ProPublica
Faizi Siddiqi, who helped start the university’s cleft team in 2003, stopped practicing last year and died from cancer in January at age 58. ProPublica was unable to reach him for comment before his death. Duane Yamashiro, an orthodontist who was the medical director of the cleft program for almost 20 years, declined through a spokesperson to comment. So did the most senior plastic surgeon currently on the team, Barbu Gociman. All three are named on the state complaint. Johns and the rest of cleft team doctors are not named on the complaint, and the hospital and the University of Utah declined to comment on it.
“We stand firmly behind our surgical approaches and believe they deliver the best outcomes for our patients, although, through an extensive review of our program we realize there are opportunities to improve the way we communicate with our patients and their families,” Wilets said in a written statement. “The safety and care of our patients is the most important thing to us.”
“We apologize for any distress to any patient family who feels we didn’t meet their expectations and did not feel comfortable addressing their concerns directly with us,” Wilets wrote.
The hospital has around 700 to 800 cleft patients at any given time, and Wilets said its cleft outcomes are in line with or better than other centers’.
In responding to concerns that patients’ families told ProPublica about, Jess Gomez, a hospital spokesperson, wrote, “We have no record of prior complaints from the families you’ve identified regarding their care, and we are saddened to learn of the concerns you’re sharing with us.” He added that the patients were cared for by Siddiqi, so the hospital is unable to respond to specifics about treatment discussions.
Innovating in surgery is a gray area. Unlike drug development, which has strict rules, surgeons are allowed wide leeway to try new things. “It’s a little bit of the Wild West,” said Dr. Jonathan Marron, director of clinical ethics at Harvard, and there isn’t agreement on what the right balance is between supporting innovation and protecting patients.
Doctors have an ethical obligation to make sure their patients are aware of how their protocol differs and what the rationale is for not doing the standard. “Informed consent, in my mind, is an important aspect of this,” he said.
As more and more doctors stick to a standard, the less acceptable a deviation from that standard practice is, Marron said. But figuring out where that line is can be difficult.
Innovating in surgery is not an area that’s robustly regulated. Last year, Utah lawmakers made it easier for doctors to practice outside the standard by loosening the rules that had restricted it, though the law still requires that patients are informed in writing and consent. The hospital and University of Utah didn’t respond to questions about whether patients are informed in writing about any deviations from the standard of care. Since ProPublica began reporting, the hospital has updated its written informed consent form regarding families’ options, Wilets said, and it now “more explicitly” tells patients that there is no standard protocol for cleft patients and different institutions have different protocols.
In other parts of the world, cleft lip and palate care has undergone changes based on government oversight. For example, in the United Kingdom there used to be many cleft centers with wide variations in success. Then the government audited outcomes, looking at factors such as how well patients were able to speak and how well their jaws aligned. Some centers achieved much better results with fewer surgeries. The government consolidated care among fewer centers to improve results and consistency. There isn’t any similar oversight in the United States.
“I think the important thing to understand here is that there’s not a whole lot of regulation in terms of who is looking after clinical outcomes,” Kirschner said. “And so it’s really [left] up to parents to do their research.”
An Outside Doctor
When Griner questioned the parents of the former Primary Children’s patients, he said, none of them understood that the treatment their child had received wasn’t the norm. The parents cycled through shock, anger and grief in his office so often that eventually he could tell by their faces what they’d say next, he said. The remorse stage was the hardest to hear, with parents blaming themselves for not asking more questions.
The parents, dogged by inchoate worries, had come to him seeking a second opinion once Griner and his partners opened their practice, he and some patients said.
Griner, who remembers going door to door to fundraise for Primary Children’s as a child, said he’d always believed that the hospital’s general excellence included the cleft team. He had wanted to work there. But Griner says that after he chose a fellowship position in Texas instead of with the University of Utah, relations soured.
Later, after seeing the unit’s handiwork firsthand in his practice, he took his concerns to the hospital’s administration. During 2018 and 2019, he said, he had three conversations with different levels of leadership, including the hospital’s then-CEO, about the poor cleft outcomes he and others were seeing. Each time, he said, his concerns weren’t taken seriously.
A spokesperson for Primary Children’s said the former CEO and another administrator couldn’t recall any such conversations, and the third, a director of surgical services at the time, said he recalled only casual conversations between colleagues. “If a concern were adequately raised by Dr. Griner, the concern would have been investigated and necessary action would have been taken,” Gomez said in an email.
As Griner’s new cleft team settled in, their worries mounted. Once a month, the cleft team would meet with patients to collectively discuss next steps. After a former Primary Children’s patient would leave one of those meetings for the first time, the doctors said they would look at each other, shaking their heads: “Can you believe that?”
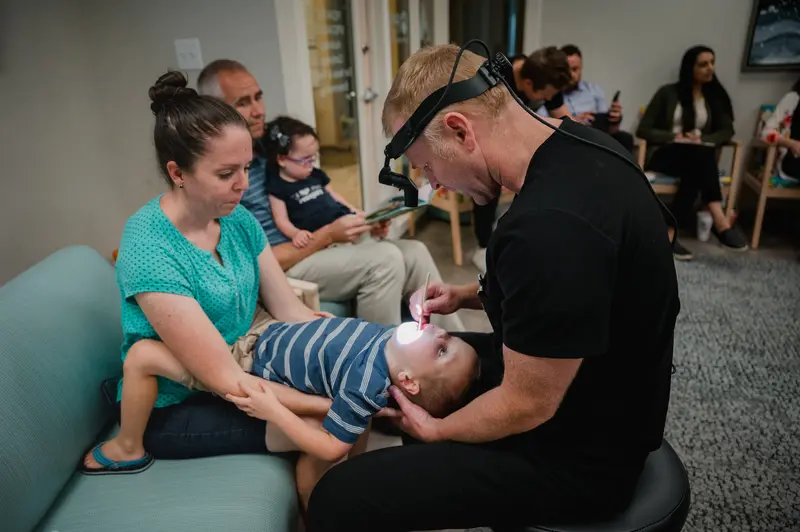
Credit:
Hannah Yoon, special to ProPublica
Primary Children’s undertakes two surgeries to repair the palate instead of one, something most doctors in the United States have stopped doing. The hospital is unusual in that it uses a prosthetic device to cover the palate hole, which requires more time under anesthesia when swapped out for a new one. The hospital also often surgically expands the palate of young patients when a retainer-like device would typically be used instead.
To Griner and his team, the timing of two major procedures — bone grafting and jaw surgeries — were worrying enough on their own, but along with other ways Primary Children’s is an outlier, they were concerned that patients were getting aberrant care at many stages.
Finally, in 2022, a group of doctors — many of whom compete with Primary Children’s — raised the issues with the state. Ten doctors’ names appear on the complaint, though one told ProPublica that although he agreed with many of the concerns, he wasn’t aware he’d been included on it.
(One of the plastic surgeons who signed the complaint, Rodney Schmelzer, has a complicated history with Primary Children’s. He lost his privileges there in 2017 and has two ongoing lawsuits against the hospital, one of which also names Yamashiro and Siddiqi. The hospital and the doctors have denied the allegations.)
Utah’s Department of Commerce, which oversees the Division of Professional Licensing, said it could not confirm nor deny an investigation.
The complaint alleges that Primary Children’s doctors “routinely exploit Cleft Patients and their families by … subjecting [them] to excessive numbers of surgeries outside the standard of care” without being honest about the risks, benefits or alternatives, which the doctors say violates medical ethics and Utah law.
Major Jaw Surgeries
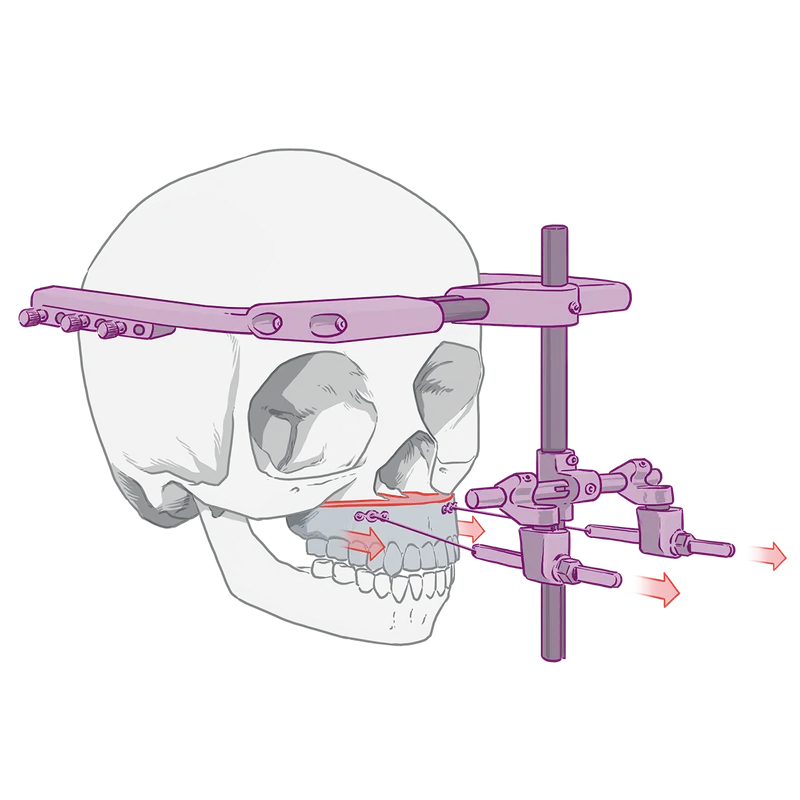
Paige Holland started looking for a second opinion when Primary Children’s said her 7-year-old son would next need major jaw surgery to correct the underbite that commonly afflicts cleft patients.
The operation, called a LeFort distraction, sounded medieval to Holland: Doctors would cut part of his upper jaw from his skull and screw a rigid metal device, called a halo, to the outside of his head. Wires would attach his upper jaw to the device, and every day for weeks Holland would turn screws to tighten the wires and slowly pull her son’s jaw bone forward and allow more bone to grow. He’d wear the halo for months.
Jaw surgeries aren’t unusual for cleft patients, but the age Primary Children’s often does them makes the hospital an outlier. Holland’s son would have been as young as 9 at the time of the surgery, according to his Primary Children’s medical records reviewed by ProPublica.
The American Cleft Palate Craniofacial Association guidelines state that “whenever possible, [jaw] surgery should be delayed until physical maturation is essentially completed.’’ Cleft doctors at six leading hospitals said they don’t perform jaw surgeries until children stop growing. For girls, that’s about 14 to 16 years old; for boys, it’s closer to 18.
Until recently, Primary Children’s website told families to expect possible jaw surgery between 9 and 10 years old. But it has since changed the age range to between 9 and 15-plus. Some other cleft centers also perform early jaw surgeries, and Kirschner told ProPublica he thinks that surgeries performed before maturity fall within the standard of care, though he personally waits for patients to be grown.
Primary Children’s data from 2020 showed that the average age of LeFort halo surgery there was 11.4 years old, according to a paper published by the hospital’s cleft team that analyzed nearly 60 cleft patients who had halos over a three-year period. The age of the patients ranged from 8 to 16 years old.
Cleft doctors ProPublica spoke with said they perform jaw surgery before maturity in only a tiny proportion of cases, usually only if medically necessary. Dr. Roberto Flores, head of the program at NYU, estimated the number at no more than 5%.
At Seattle Children’s Hospital, even in those extraordinary cases, the surgery would not happen until 12 to 14 years old, when most of the adult teeth are finished coming in, according to the hospital’s former chief of craniofacial surgery, Richard Hopper.
“I’ve been with the cleft team for 20 years, and I can pretty conclusively say we haven’t done a Lefort … on a patient younger than 12 years old, 11 at the earliest,” Hopper said last year before he took a job with Texas Children’s Hospital.
“The earlier you do a jaw surgery, the more likely you’re going to have to repeat it later,” a cleft team surgeon at a top-rated pediatric hospital said. “Basically you’re committing kids to having an extra operation.”
The best practice, many doctors said, is to do one definitive jaw surgery close to adulthood.
“It’s a brutal enough operation. You wouldn’t want to have to do it twice,” a leader in the field said. Both doctors asked not to be identified out of concern it would jeopardize relationships within the small community of doctors who provide cleft care.
Primary’s Johns said such critiques ignore the psychosocial issues children with cleft deal with. Bullying should be given more weight in treatment plans, she said, and repairing a child’s differences before high school has merit. Most of her surgeries wait till at least age 12, she said, and when she does them on younger patients, it’s for either psychosocial or other pronounced medical problems.
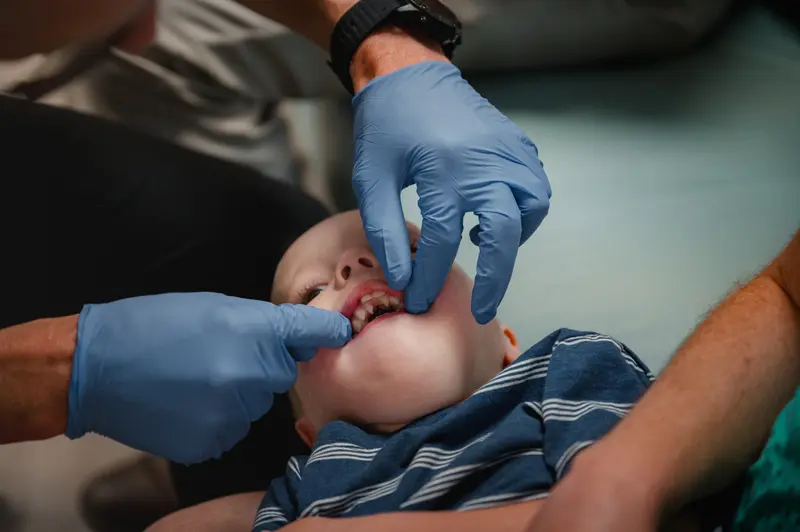
Credit:
Hannah Yoon, special to ProPublica
Moreover, patients who wait until maturity can sometimes require extensive operations involving both the upper and lower jaws, Johns said. Patients who’ve had the surgery young might require a second jaw surgery, she said, but it would involve only the upper jaw. The trade-off, she said, is worth it.
Rohit Khosla, surgical director of the cleft team at Stanford Medicine Children’s Health who trained Johns during her fellowship, reviewed all of the hospital’s protocols at her request. In general, Khosla told ProPublica that he thought the hospital’s methods were controversial but not problematic. He found several problems with the cleft team’s study designs and conclusions, but overall its “protocols are conscientiously thought out with [a] goal to provide a high level of care,” he said in a summary of his report. The hospital would not share his full written review and asked Khosla to stop speaking with ProPublica once it was completed. Primary Children’s also set up a double-blinded review — neither the hospital nor reviewer knew whom the other was — to further assess its protocols, but the hospital said it would not make the report public when it was completed.
In looking at the hospital’s latest LeFort data, Khosla wrote that in the “last few years” the average age has increased to 14, “which I find more acceptable.”
On a Facebook page for Utah parents of children with cleft, numerous posts over the years speak to the hospital’s push to perform LeForts young. Some talk about how their children endured the surgery before 10 years old — “not going to lie the Halo is tough!” one mother wrote — and needed to repeat a jaw surgery as a teenager.
Holland said she thought there had to be another way to fix her son’s underbite and asked about braces. After Primary Children’s said there wasn’t, she said, she sought a second opinion with Griner, who sent him to an orthodontist instead. Holland’s son was one of at least seven former Primary Children’s patients whom Griner said he diverted from having surgery before maturity. None of them, in Griner’s opinion, had any medical necessity for the operation before maturity or reported bullying or other psychosocial issues. Schmelzer, who also signed the complaint against Primary Children’s, said his medical records showed similar numbers.
Griner recalled one startling case last summer in which Primary Children’s had lined up surgery for a 9-year-old child whose jaw was nearly normal. An independent plastic surgeon who specializes in cleft at a large academic institution reviewed the patient’s CT scan for ProPublica and confirmed Griner’s assessment that there was no need for surgery.
Holland’s son, now 13, has only a minor underbite after orthodontics and likely won’t need jaw surgery at all.
“He’s totally fine,” Holland said. “He was saved from a major surgery.”
Experimenting With Bone Grafts
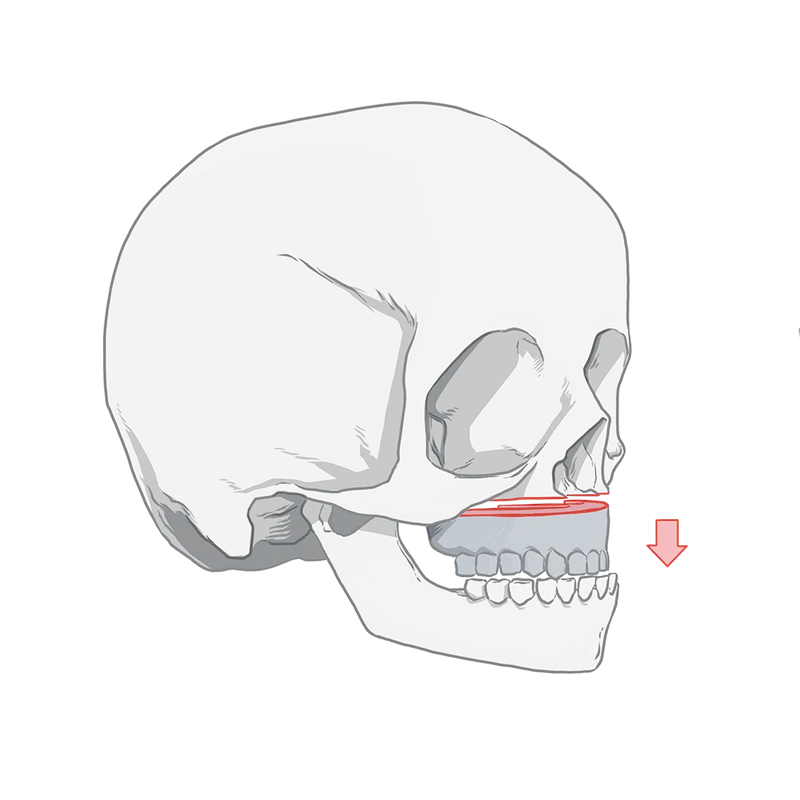
About seven years ago, spurred by what Johns said was a “hypothesis we had,” Primary Children’s cleft team began experimenting with how surgeons bone grafted the upper jaw.
Without putting in place the protections of a formal research study, Johns and her colleagues decided the invasive surgeries could be done successfully when children were years younger — age 2 — than was standard practice in their field.
The “gold standard” for a bone graft is to use a piece of the child’s own hip. At 2, a patient doesn’t have enough bone to harvest. So over a period of about two years, Primary Children’s tested in its toddler-age patients different combinations of materials that would create a lasting bone graft.
Among the materials was a controversial product called bone morphogenic protein, or BMP, which stimulates bone growth. The BMP is put into the jaw where the child is missing bone and, in theory, spurs the body to naturally make bone, gradually filling the gap.
Some cleft doctors have hailed BMP as a less invasive way to treat patients since it first came to market in 2002 — but Primary Children’s believed it could be used in children years younger than their peers at other centers.
The parents of several patients told ProPublica they were never informed that their child was undergoing an untested procedure. In some cases the bone graft failed, necessitating a repeat of the painful operation.
In 2017, Gavin Rogers, 21 months old with the wispy blond hair of a baby, had bone graft and hard palate repair. Afterwards, “he was screaming all the time. He wasn’t sleeping, wasn’t eating. I had to squirt milk into his mouth,” his mom, Emily Rogers, recalled.
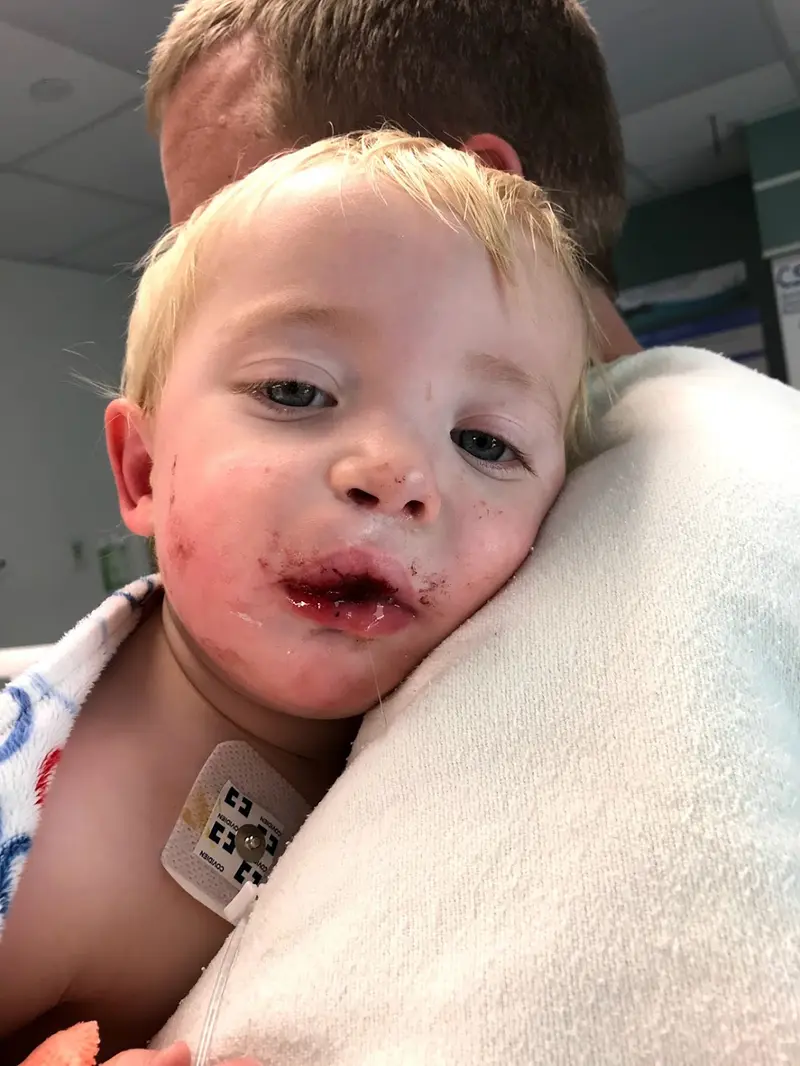
Credit:
Courtesy of Emily Rogers
Primary’s decision to use BMP in toddlers was a risky bet. In 2015, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration issued a safety warning about using BMP in children. The warning said that BMP hadn’t been approved for children “because their bones may still be growing and using this product may cause serious injuries.” The FDA action followed revelations of injuries, including alleged deaths, related to the use of BMP in spine patients. BMP’s maker was subjected to a congressional investigation and paid hundreds of millions to settle civil suits.
The FDA recommended against routine use in children and told doctors to be sure to inform parents about the risks.
Doctors are allowed to use products like BMP for so-called off-label purposes and commonly do, often to the benefit of their patients. In 2017, Dr. Jeff Hammoudeh, a plastic surgeon at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, published one of the largest studies of BMP in cleft patients and found that over nine years of use its safety and success was comparable to using bone from the child’s hip. But the average age of his patients was 11 and his youngest patient was 6. He said he wouldn’t use BMP in patients any younger than that because of concerns, shared by other experts, about the long-term growth of a child’s face and questions about the safe amount to use in a child of that size.
Johns, of Primary Children’s, said that Hammoudeh’s study was one of the reasons her team felt confident in using BMP.
Hammoudeh said doctors need to be up-front about what they are doing and build in clear guardrails. When he experimented with performing lip repairs in newborns, he did so through a supervised research study. Parents, he said, were given the choice to have the traditional protocol, just as they were for bone grafting with BMP.
Some doctors may eschew the word “experiment” when trying out a new protocol, he said, but that’s what it is — even if they deem it “innovation.”
“You can soften the terminology any which way, but if you don’t know what the results will be, you don’t know what the results will be,” he said.
Johns told ProPublica she doesn’t offer parents the choice to have a bone graft at the traditional age because she’s confident that her way is better. Giving them the option, she said, “means that we’re telling them, ‘OK, we’re going to allow you to have subpar results.’”
Johns said that since as early as 2018, the parents of patients have been told that the new protocol is superior to traditional care, a claim she said is supported by observational results from the team’s first patients.
The Rogerses and other parents who spoke with ProPublica said Siddiqi, the lead plastic surgeon at the time, led them to believe that grafting at toddler age was the standard of care.
“One hundred percent,” said one mom, whose daughter was not yet 18 months at the time of the procedure and had to repeat the surgery later. She said the conversation with a reporter “was the first I’m hearing this isn’t typical.”
After his surgery, Gavin happened to see a new doctor outside the hospital. Rogers said she stopped breathing when she learned that around the country, many doctors time bone grafts to when certain adult teeth come in. Gavin still didn’t have all his baby teeth.
And the bone graft didn’t work. Gavin faces a second bone graft surgery this summer at 8 years old — in the age range when most other doctors would have done it the first time.

Credit:
Hannah Yoon, special to ProPublica
Four years after Primary Children’s started the protocol, the hospital did its first formal study — a review of 14 patients’ medical records. From around 2017 to mid-2019 — when Johns was telling patients the protocol was a success — the cleft team used different surgical techniques and a combination of bone products, including the BMP, that proved unreliable, and some patients needed additional grafts, according to the study and a university spokesperson.
A hospital spokesperson said its bone grafting procedures have advanced since patients such as Gavin had the operation. Khosla, the Stanford doctor who reviewed the protocol, reported in his summary that newer hospital data demonstrates good early results.
Johns and Agarwal said their new protocol was a slow evolution and didn’t need to be overseen by independent reviewers. Performing a bone graft sooner, they said, would solve a common problem in cleft patients in which the arch of their mouth is narrow and collapses inward as they grow. Moving to age 2 was a minor progression, Johns said, noting that the mouths of a 5-year-old, the youngest age most doctors would do a bone graft, and a 2-year-old are similar.
“There was nothing that felt outlandish about it,” Johns said.
Johns concedes they don’t know yet how their patients’ faces will grow over time. So far, she said the outcomes are trending in the right direction, “but we recognize that we’ve got eight more years to continue to see if it holds up.”
She’s clear about this uncertainty with her patients, she said, as well as how Primary’s protocols diverge from the standard. She said if parents are uncomfortable, she encourages them to seek a second opinion. (One mother said Johns’ colleague told her that he would no longer treat her son after she sought a second opinion.)

Credit:
Kim Raff, special to ProPublica
Jessica Bernstein, whose 6-year-old son is a cleft patient at Primary Children’s and whom the hospital connected with ProPublica, said she had the utmost confidence in the care received and felt Johns and the other doctors carefully thought out decisions. She said they told her that the hospital’s timeline for care was based on the latest, best research. Although she said she wasn’t informed that aspects of the hospital’s protocol differ from the standard or that BMP was off-label for children, she felt her son was being treated in the right place.
Other cleft doctors said previous attempts to fix the upper jaw line between birth and 2 years old — known as “primary bone grafting” — were abandoned because of poor outcomes.
Dr. Ron Hathaway recalls when he was at the University of Indiana and participated in a study that compared outcomes at five cleft centers. One fared significantly worse. The upper jaws of many of its patients didn’t grow as expected, leaving them with underbites. Hathaway was stunned to learn it was his program.
Indiana, it turned out, was the only one that grafted before age 2. The others waited until patients were school age. Hathaway had been involved in such grafting at Indiana since 1992, and now he faced the humbling data that his patients were three times more likely than the study’s best center to need invasive jaw surgery because of it.
“I had to go home and have a serious conversation with my surgeons,” he said.
Indiana eliminated primary bone grafting, and when the study was repeated 10 years later, Hathaway said, outcomes had drastically improved. While this type of research can’t definitively prove causation, he said, “a thinking person would say primary bone grafting causes [poorer growth] of the upper jaw.”
The original study was published in 2011, joining a body of research over decades that showed such grafting was “significantly detrimental,” Kirschner, of Nationwide, said.
Nevertheless, in 2016 the cleft team at Primary Children’s began questioning whether operating earlier would be better, said Agarwal, the chief of plastics. He and Johns said what they do is different — in terms of a slightly older age and specifics of the procedure — from the primary bone grafting of the past. Khosla, of Stanford, wrote in his review summary that the protocol challenges conventional wisdom, but “their rationale and the theoretic benefits are sensible.”
For Cindy Anderson, whose daughter’s bone graft echoed Gavin’s in both timing and failure, it wasn’t just that her daughter had to repeat a surgery. Had they been informed of the innovative nature, Anderson said they might have agreed because of their faith in the doctors. But not to be given a chance to consent made them feel duped.
She said they’re left wondering about Primary Children’s: “What the heck are they doing?”
Mariam Elba contributed research.